Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
The Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) is one of the two main performance indicators for a regression predictive model. It measures the average difference between values predicted by a predictive model and the actual values. It provides an estimation of how well the predictive model is able to predict the target value (accuracy).
How to interpret the indicator?
The lower the value of the Root Mean Squared Error, the better the predictive model is. A perfect predictive model (a hypothetic predictive model that would always predict the exact expected value) would have a Root Mean Squared Error value of 0.
The Root Mean Squared Error has the advantage of representing the amount of error in the same unit as the predicted column making it easy to interpret. If you are trying to predict an amount in dollars, then the Root Mean Squared Error can be interpreted as the amount of error in dollars.
How to decrease the Root Mean Squared Error?
You can improve the Root Mean Squared Error by adding more influencer in the training data source.
What is the formula used to calculate the Root Mean Squared Error?
The Root Mean Squared Error is calculated using the following
formula: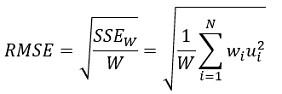
where:
SSEw = Weighted Sum of Squares
W = Total weight of the population
N = Number of observations
wi = Weight of the i-th observation
ui = Error associated with the i-th observation
Other Interpretation
The Root Mean Squared Error can be interpreted as the standard deviation of the error (it's the square root of the error variance).