Measure-Based Filters
You can create story and page filters based on a range of measure values.
For example, if you want to include in your story only those company employees who earn between $50,000 and $100,000, you could create a filter based on the Salary measure.
When you use a measure-based filter, you need to specify one or more dimensions for aggregation context. In the above example, you could choose the dimension EmployeeName for context.
Or, if you're analyzing salaries of company employees based on country and gender, you could choose the two dimensions Country and EmployeeGender for context.
- You can base filters on calculated or restricted measures.
- Calculated dimensions and the Date dimension can't be used for the dimension context.
- If a model has a version or category dimension (all planning models, plus some HANA analytic view models), the version dimension is automatically added into the dimension context and cannot be removed.
- All required dimensions are automatically added to the dimension context.
- If a hierarchical dimension is added to the dimension context, the data is aggregated at the booked nodes.
- Measure-based filters are available with import data connections, and live data connections to SAP HANA.
- These calculations can be used to set up a measure-based filter:
- Restricted measures
- Calculated measures
- Difference from
- Aggregation
- Measure-based filters can't be used within an advanced filter.
- Planning operations are disabled for tables that have measure-based filters applied.
- Measure-based filters won't affect value driver tree widgets.
- Dynamic image objects don't support measure-based filters.
Filter Evaluation Order
If a story is not hosted inside a Digital Boardroom presentation, then filter evaluation starts at the story filter level, then proceeds to the page filter level, and then to the widget filter level. If a story is hosted inside a boardroom presentation, then filter evaluation starts with the topic filters first, and then proceeds to the story, page, and widget filter levels.
Filters are evaluated per level. For example, if the story-level filter is defined as “only countries with sales greater than $10 M”, and the result of that filter is USA, Canada, and Germany, then the page-level filters would filter data from only these three countries.
Within a given level, there are two steps in evaluating dimension-based filters and measure-based filters:
- All dimension-based filters are applied first, by combining them together using AND logic.
- After that, the remaining measure-based filters are evaluated based on the result of the dimension-based filters. All the measure-based filters are combined together using AND logic.
Controls Panel
When several types of filters are applied to a story, it can be difficult to understand which order the filters are applied in. To show the filter evaluation order visually, the Controls panel displays all of the filters that apply to the story.
To open the panel, select Controls, or from a widget's action menu, select , or select a filter and then select View Controls.
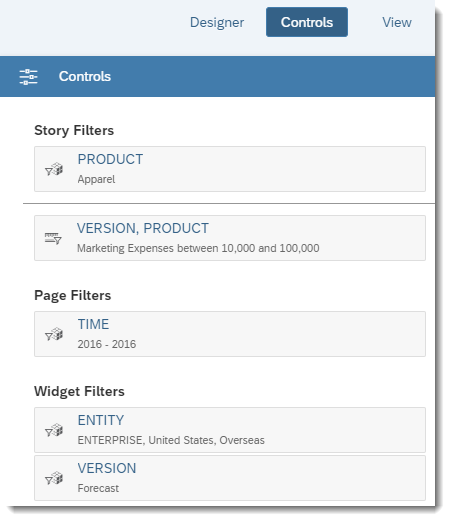
Filters are applied from top to bottom. In this example, the PRODUCT filter is a dimension-based filter, which is applied before the measure-based filter VERSION, PRODUCT. To view more detailed information about each filter, point to a filter token and select .
Note that the Controls panel only displays the filters; you can't edit the filters directly from the Controls panel.
Once the Controls panel is opened, you can select other widgets to see which filters are applied to them. The Controls panel updates automatically as each widget is selected.
The Controls panel is available in both Edit mode and View mode, and with all page types (grid, canvas, and responsive).

 View Controls
View Controls