Choose Between Datasets and Models
Depending of your business case, you can choose between preparing your data using a model or a dataset.
Before building your story, you need to make sure that your data is prepared for scenario analysis. With SAP Analytics Cloud’s wrangling experience, data preparation can be done using either dataset or a model.
The graphic below summarizes the main differences between a model and a dataset:
This image is interactive. Hover over each area for a description.
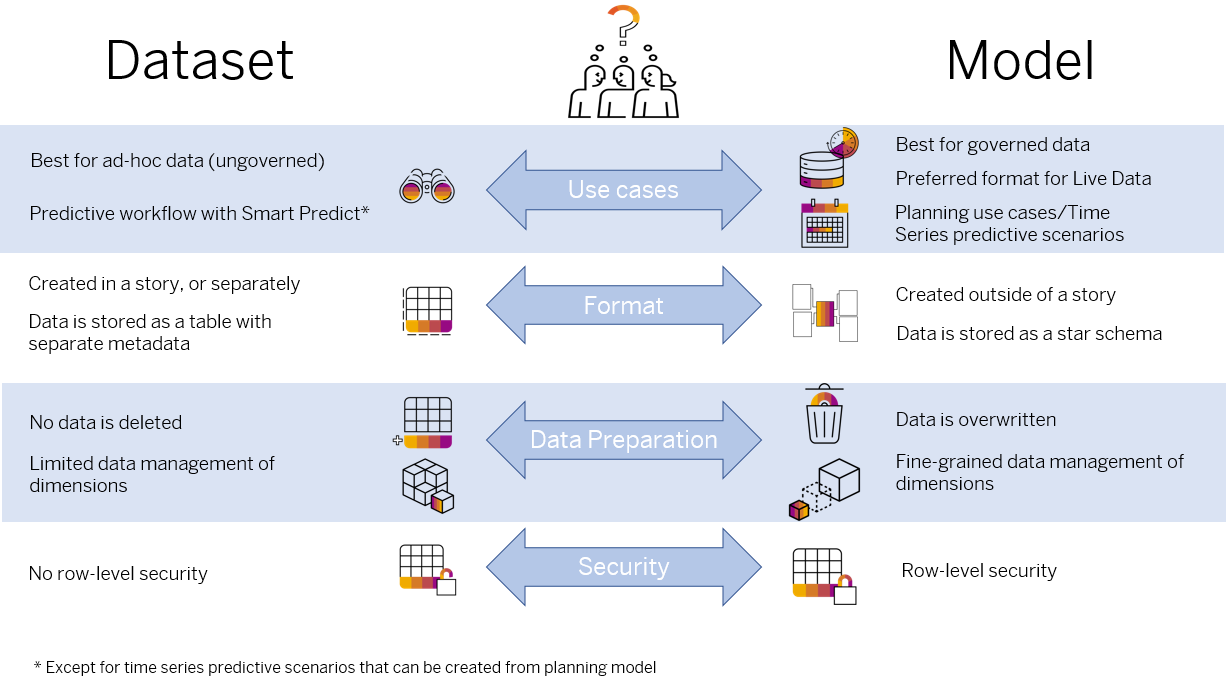
Identify Which Format Fits Best Your Needs
Datasets store data in a single table, and the semantic structure is defined by the metadata. Go for a dataset if you’re only looking to upload data, using a .csv or .xlsx file, and analyze it in a story straight away.
Models store data as a star schema, and the structure of the model is reflected in the database. Go for a model if the structure of the data is already set, or if you already have a structure in mind before importing the data to fit into the model. A model is preferred when it comes to govern the data processing, like in case of planning.
Advantages of Using a Model
Models guarantee that the data they hold follows a series of business rules that certify that workflows such as planning can be run. Changes made to the structure of the model can be done either at the structure level, if the fact table is empty, or by rebuilding the model from the original data preparation session.
Models also support row-level security, fine-grained data management of dimensions, and fact tables.
Advantages of Using a Dataset
Datasets are reactive to change, any modifications you make to the data or data structure are done simply by editing the dataset, without data loss or restriction.