About Datasets and Dataset Types
A dataset is a simple collection of data, usually presented in a table. You can use a dataset as the basis for your story, and as a data source for Smart Predict.
Dataset are first choice when you want to create story/ visualization quickly and do not want to get into structure definition, during data processing or when development do not demand IT governance. In SAP Analytics Cloud, you can encounter different types of datasets:
Embedded Dataset
When you create a story and import data from a file or other data source, but not from an existing saved model or dataset, that data is saved as an embedded dataset (also called a private dataset) within the story, and this dataset doesn't appear in the Files list. However, if you want others to be able to use this dataset, you can convert it to a public dataset:
- In the Grid view (
 ), select
), select
 (Convert to Public
Dataset).
(Convert to Public
Dataset). - Type a dataset name, and a description (optional). And select OK.
Standalone Datasets
This type of dataset is stored in SAP Analytics Cloud and you can find it in a folder location (for example, public, private, or workspace) on the Files page. You create them collecting your data either by importing a data file or collecting files from other systems.
Datasets for Smart Predict
Dataset can be used as data source for Smart Predict. However, they must have a certain structure and must contain some mandatory information depending on the type of predictive scenario you are creating and where you are in the modeling process. Each row represents an observation (which is the object of your interest), and each column represents information corresponding to this observation. One of the columns represents the target variable.
Depending on the nature of the data contained in the dataset, you will be able to leverage it to create a certain type of predictive model for your specific need.
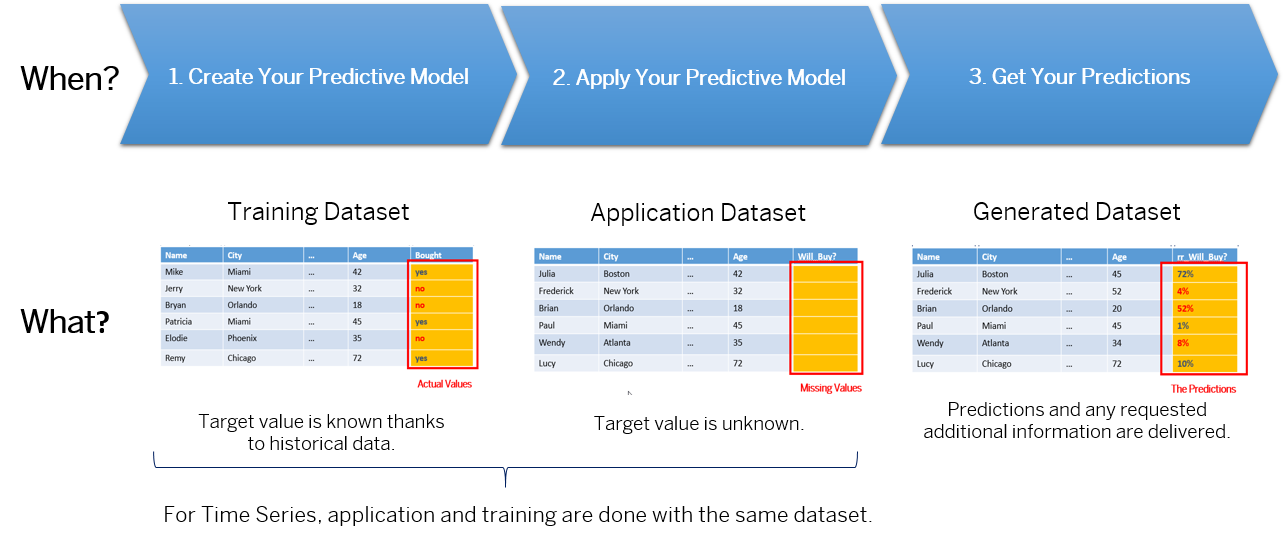
The graphic below summarizes which dataset is used depending on the step of the predictive process:
Input Datasets
- Acquired: Data is imported (copied) and stored in SAP Analytics Cloud. Acquired dataset have already been prepared on your computer (supported formats are .TXT, .CSV and .XLSX ).
- Live: Data is stored in the source system. It isn't copied to SAP Analytics Cloud, so any changes in the source data are available immediately if no structural changes are brought to the table or SQL view. You can connect to live data and create a live dataset.
Depending where you are in the predictive model lifecycle, your input dataset can be a training or an application dataset (in the case of a classification or regression predictive model) or both (in case of a time series predictive model as only one dataset is used).
An input dataset is used to train the predictive model (training dataset) or is used to apply the predictive model (application dataset).
Training Dataset
The training dataset contains the past observations that will be used to generate the predictive model. In this set, the values of the target variable, which is the variable corresponding to your business issue, are known. By analyzing the training dataset, Smart Predict generates a predictive model that explains and predicts the target variable, based on the variables identified as Influencers.
Application Dataset
You apply a predictive model on an application dataset (for classification and regression predictive models).
- The same number of variables (additional columns will be ignored),
- The same variable names as the corresponding training dataset.
Generated Datasets
When you click the Apply button to get your predictions, a dataset containing your predictions is generated. You can choose in which directory you want to save your dataset. By default, they are saved in this folder: .
- If both datasets have identical variables, the new dataset will automatically replace the existing one.
- If the datasets are different, you receive an Apply Failed message. To continue, save your dataset under a different name.
The generated dataset contains the predictions and any additional columns you have requested.
Video: How to Create Datasets or Stories with Embedded Datasets
Open this video in a new window
In this video, you will create a standalone dataset, perform data wrangling, review the measure and dimension properties, review the data transformation and enrichment options, and see how to create an embedded dataset in a story.