Learn About Models
A model is a representation of the business data of an organization or business segment. You can use a model as the basis for your story. The Modeler is the place where you can create, maintain, and load data into models.
In SAP Analytics Cloud, models can either have acquired data, or live data:
- Acquired: Data is imported (copied) and stored in SAP Analytics Cloud. Changes made to the data in the source system don't affect the imported data.
- Live: Data is stored in the source system. It isn't copied to SAP Analytics Cloud, so any changes in the source data are available immediately if no structural changes are brought to the table or SQL view.
Models complement datasets. Datasets are more suitable for ad-hoc analysis, while models are more suitable for governed-data use cases.
If you're not sure whether to use a dataset or a model for your story, this might help you decide: Choose Between Datasets and Models.
If you're more interested in datasets, not models, see About Datasets and Dataset Types.
What's in a Model?
- Quantities of each clothing type sold
- Prices of the clothing items
- Item descriptions and ID numbers
- Order dates
- Customer names, ID numbers, and locations
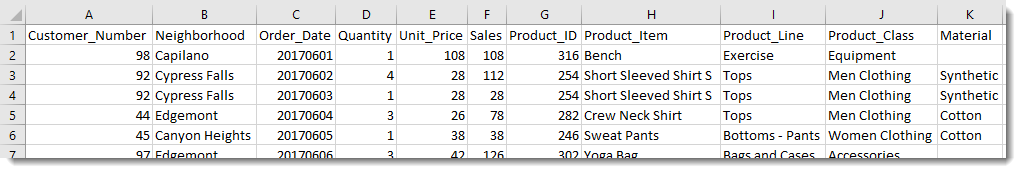
The picture above represents a small subset of data.
Typically, your business would generate thousands of rows of data. To avoid dealing with these large amounts of data that would require using a database query language such as SQL, you create a model with dimensions and measures to represent your business data and manipulate them directly in the application. The creation of a model is a crucial part of the data preparation.
So, what exactly are dimensions and measures?
Measures hold numeric values and typically represent quantities that provide meaning to your data. For example, sales revenue, salary, or number of employees. Dimensions on the other hand represent categories that provide perspective on your data. For example, product category, date, or location.
Before getting into further details about dimensions and measures, you should know that two types of models are available: analytic models, and planning models.
Selecting the Right Model for Your Data
When creating your first model, you first need to decide between the two models types that the application has to offer: planning models and analytic models. You can create analytic models from a live data source but you can't create planning models from a live data source. However, live models created based on live connection to SAP BPC embedded configuration support planning functionalities.
Planning Models
- Categories for budgets, plans, and forecasts.
- Default time periods that you can quickly adjust to suit your data.
- Auditing features for traceability.
- Security features that make it possible for you to restrict access to specific values in data grids to named individuals.
When working with this type of model in a story, planning users can use a variety of features to update values in the model, and create new values.
Analytic Models
Analytic models are full-featured models that contain your business data. They're the more flexible type of model. You'd typically use an analytics model if you want to analyze your data, looking for trends and anomalies. Unlike the planning model, analytic models are not preconfigured with categories (for budget and forecast data), and although a Date dimension is available, it's not required, and you can remove it from the model during the design stage.
Analytics models can also be used with live data connections. For more information, check out Live Data Connection Overview Diagram.